Series and Parallel Circuits
How to Simplify to Find
Total Resistance, Current and
Voltage
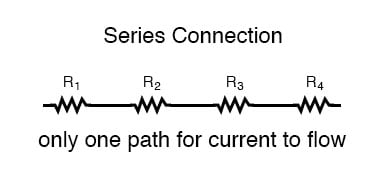
Series Circuits - Series Circuits are the simplest to work with.
• Here we have three resistors of different resistances.
They share a single connection point. When added
together the total resistance is (R1+R2+R3+R4) -Ohms.

Calculating Total Resistance of a Series Circuit
As the resistors are connected together in series the same current passes through each resistor in the chain and the total resistance, RT of the circuit must be equal to the sum of all the individual resistors added together

Solving the above equation for total resistance (instead of the reciprocal of total resistance), we can invert (reciprocate) both sides of the equation:
Parallel Circuits - A parallel circuit is shown here and it has TWO
common connection points with another component.
In this case another resistor. We cannot add the
values of each resistor together like we can in the
previous series circuit.

Calculating Total Resistance of a Parallel Circuit
Two methods can be used to calculate the total
resistance of the parallel circuit. They are the
Product Over Sum equation or the Reciprocal
Formula.

The same basic form of equation works for any number of resistors connected together in parallel, just add as many 1/R terms on the denominator of the fraction as needed to accommodate all parallel resistors in the circuit.


0 Comments
Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box.
Emoji